Scene Tree Editor
Table of Contents
When working with nested scenes and remoting, one can easily lose one's overview of which scene is rendered where. That is why Ventuz provides the Scene Tree (SHIFT-F12):
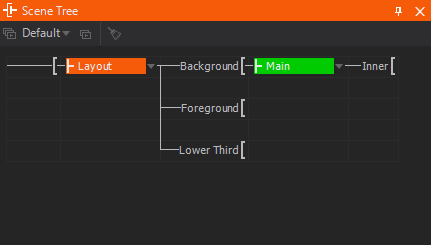
This editor shows all scenes in memory along with their available ports. Scenes can be loaded by Ventuz Designer, by a Port node or by Remoting. The editor uses a tree-like visualization similar to that used in the Hierarchy Editor. Drag&Drop makes it easy to assign scenes to Ports and track assignment changes via Remoting. The scenes currently opened in the Designer as well as the current Layout scene are visually marked in the Scene Tree Editor. The screen-shot above shows following situation:
- The Layout scene 'Layout 1' has 3 Scene ports: Background, Foreground, Lower Third.
- The Port 'Background' is selected as the Port where new scenes are assigned to (bold font).
- Scene 'Main' is assigned to Port 'Background' and is active/rendered in this Port.
- Scene 'Main' contains another Scene Port ('Inner') which has loaded the scene 'Inner'.
- Scene 'Layout' is the active document in the Designer so it is marked orange
- Scene 'Main' is part of the rendered tree and therefore marked in green
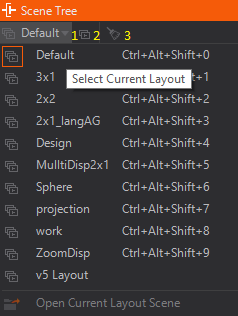
- (1) Inside the Scene Tree Editor one can switch the Layout to be used by the current project (see below)
- (2) as well as open the currently used Layout scene for further editing inside the Designer.
- (3) When you work with Remoting all unused Scenes loaded by Remoting can be released.
Remoted Scenes
Whenever a scene is loaded by one of our available Remote Interfaces or through the Template Engine, the Scene is marked by a red dot. Those scenes are always kept in memory until either the remote program is unloading the scene or the clean up button is pressed.
Layout Scenes
A Layout is a scene loaded by the project in front of the first 'user-scene' on Level 1. Layouts are placed on Level 0 and can be used to create multiple ports the Director can cue and take templates to (see Director Multichannel), do more complex setups or do global data processing.
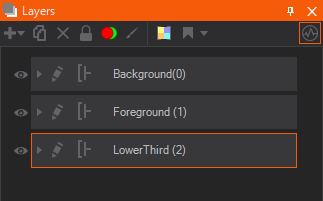
Layouts are usually very simple scenes holding at least one unlocked Layer Port. Generally, Port Ordinal 0 (the default port) is not locked. A Layout scene is a normal scene: one can use all nodes, add properties to Project and Scene Data and insert layout related content. The possibilities of Layouts are numerous:
- A Split Layout with two ports (left and right) by using two Layer Nodes and adjust the Layout.
- A layered scene Layout: imagine three Ports: Background, Content and Overlay!
- An effect-layout making a standard set of Effects!
Layout scenes opened in the Designer via Scene Tree Editor are marked with a special icon in the scene tab!
The configuration of Layouts is done in the Project Properties. The Layout section in the Project Properties dialog provides possibilities to create and edit Layouts.
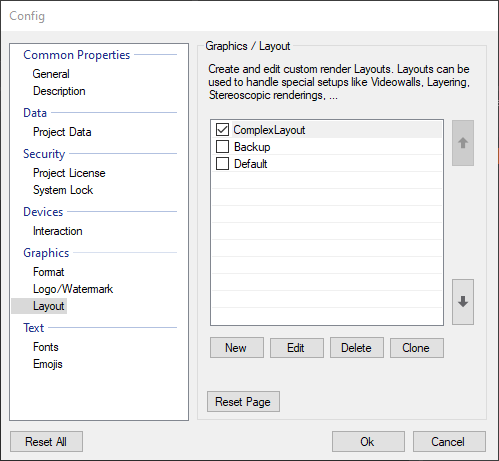
A Layout setup is created by clicking the New button. In the General tab, a name for the Layout and the actual Layout scene file can be chosen. The fields Description and Icon can be used to help other users who work on the same project.
The Machine Tags property is a list of comma-separated three-character-codes. They are used to determine which Layout will be used on the current machine. Each machine has a Machine Tag that is defined in its Ventuz Configuration. Once the Runtime is started it will search for that tag in the Layouts - if no tag is given or it is not present in any Layout, the default layout will be used: Every entry in the Layout list has a check-box. The checked Layout is selected as the Runtime Layout which is automatically used if a scene is exported as Presentation (VPR) or the Ventuz Runtime is started in Director mode and no tagged Layout is used.
Interfacing
Interfacing allows for communication between Layout scenes and the inner scenes loaded via the corresponding Port Nodes. The properties which should be used for the inter-scene communication have to be exposed on Layer level. To create the interface counterpart on Layout scene level, an inner scene with the appropriate exposings has to be loaded to a Port.