Content References
A typical approach to Director is to at first see it as an application that is used on-the-fly: Cue template, change values, take to air, cue template, changes values, take on air and so on...
However, the bigger the shows becomes, the more it becomes important to actually plan ahead and prepare or even re-use intermediate results. This is where Pages, Playlists and the Timeline come into play. Even when using those more advanced features, a user might be tempted to think of a page as something static that is created once and never changed again. This chapter will introduce the concepts of content references which allow the operator keep modifying existing content and having the rest of the show update automatically.
The Property Editor Continued
What has been omitted in the previous explanations of the Property Editor is the arrow icon in the top-left corner of the Property Editor. This represents a reference to another content element inside Director. For example, when cueing a template by double-clicking on a thumbnail in the Template Browser, Director keeps track that the template instance was created based on that blank template. This is called a reference. When hovering the mouse cursor over the icon, a popup will appear that lists the reference for the template instance.
Depending on how the cued content was created, there can be further icons to the left of a template name. In the example below, the part below "Show Opener" has been created based on a Playlist Entry (four vertical lines) and the part "Score + BannerSponsor" based on a Sub-Page. To make it easier to spot which parts belong to which, a box is drawn around the respective areas.
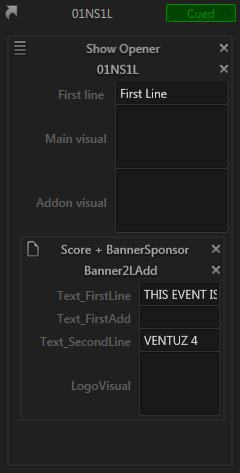
So what are the consequences of having such reference? For one, they are used as basis for detecting modifications by the user. For a part of the content that comes from a page, the saved version of that page is what the local modifications are compared against.
The other advantage of references is automatic updating:
If a content - such as a page - is modified and then saved, all unmodified uses of that content are automatically updated to the new version!
For example, imagine a sub-page that has been prepared for a specific sponsor. It has been created well in advance since it will be used multiple times within the show. To be more specific, it in fact has already been used when the whole show was pre-scripted in the Playlist or Timeline. What if just before the show a new logo for that sponsor is handed in? Simple: As long as the playlist/timeline use the page without any local modifications, modify the original page and save it back to the page. All unmodified references will update automatically!
Editing and Saving
This brings us back to the footer in the Property Editor. How does one modify a page and not just the template instance the page is used in? Both actually amount to the same thing! First, cue the content:
- Page: For pages, cue them by double-clicking on them in the Pages Browser.
- Playlist: double-click on the playlist entry to edit.
- Timeline: Select the item to be modified in the Timeline window.
This should show the content in the preview window as well as in the Property Editor. Perform the desired modifications and then click the save button in the footer of the Property Editor. The modification markers (red bars) to the left of the data fields should disappear. If there are multiple targets for a modifications (e.g. a Timeline Item that references a playlist entry and has added a page), a context menu will open up asking the operator to choose the target.

Changing Properties (such as the name, description, keywords, ...) of a content is done in a similar fashion. Again, get the content into the Property Editor and then press the edit button in the footer.
Opposed to changing template values, changing properties is done directly and does not require pressing the save button.
Embedding & Reverting Content
Sometimes it is desirable to have a template instance completely independent of other content. This is called embedding the content. It is represented by two document shapes overlapping each other instead of the arrow in the top left corner of the Property Editor:
The inverse operation is reverting the content. This will throw away any local modifications and rebuild the template data based on the referenced content. Both can be done for playlist entries and timeline items via the respective main menu entry.
Timeline items with local modifications are automatically switched to embedded contents upon saving a show to prevent data loss.