Analyze Audio
 | Analyze Audio | This node analyzes sounds and provides a . |
Ventuz provides real-time audio analysis for creating graphics that react to sound sources. This can be used to create custom graphical equalizers of any kind of show and exhibition enhancements with audience interacting with the graphics via sound. The Analyze Audio node analyses the audio frequencies of a sound source and outputs the result as either an array or a texture.
The property Channels defines which stereo channel should be analyzed. You can either use the Left or Right channel, a sum of both (Mid) or the difference (Side). The Ordinal property specifies the audio capture device that should provide the audio data for analysis. Gain adds an offset to the output to create enough contrast in loud or quiet sounds.
Analysis
There are three different options of what can be analyzed. You can change that by adjusting the Analyzer property group.
Scope
Scope will return the sampled waveform of your audio source. Size defines the count of samples in each frame. 800 creates just as many samples as your audio source if it has a sample rate of 48kHz at 60 frames - 48000 / 60 = 800. More samples would not affect the accuracy anymore. Sync To Zero Crosspoint will move the resulting waveform so that the nearest sample to the center of the waveform will be zero. This is purely cosmetical. High Cut will remove high frequencies from the waveform while sampling so that the result will look smoother but has less details.
Spectrum
Spectrum returns the samples of a Fourier Transformation of your audio source representing the different frequencies of your waveform. Bands changes the amount of resulting values. Using a linear distribution of samples will result in less detail in the higher frequencies (we perceive frequencies in a logarithmic manner), to compensate for that you can use one of the logarithmic distributions of samples in Bands. The Logarithmic flag will enable a logarithmic scaling of the resulting values - this makes sense in most cases since volume is perceived logarithmically as well. If turning on the Logarithmic flag you need to define the Floor volume that is the minimum shown resulting level. By changing Falloff you can define a delay in the decrease of the results, the increase will still be immediate. 100% means immediate falloff, 0% will never decrease again.
VU Meter
VU Meter will simply return the overall volume of your sound as single value. Using the Mode you can either choose to search for the Peak in the last time Window or you can analyze the average amplitude of the sound with the RMS mode (Root Mean Square). Again you can scale the output logarithmically to compensate for the logarithmic perception of loudness. If turned on you need to define the Floor as well. By changing Falloff you can define a delay in the decrease of the results, the increase will still be immediate. 100% means immediate falloff, 0% will never decrease again.
Output
You have different options to output the gathered data.
Data
The Data property group will output an array with as many elements as defined in the Analyzer property group. Additionally it will return the Sum of all values.
Note that processing Arrays in Ventuz oftentimes is a lot slower than using Textures - so in most cases the Texture Output property groups are preferred. Especially when using a Particle System as a destination for the outputs of this nodes you should decide to work texture based directly.
1D Texture
The 1D Texture property group returns a texture with a size of 1 by as many pixels as you have samples in the Analyzer property group. You can change the Format to either only write to the Red Channel of the texture with 8-bit integers (R8) or with 16-bit floating point numbers (R16F). Lastly you can sample from a Gradient depending on the Output value using the RGBA8 method. Vertical changes the orientation of the texture.
2D Texture
The 2D Texture returns a texture just like the 1D Texture, but will keep the results of the last few frames and add it to the second dimension of the texture. Thus all properties work the same. History Size changes the number of saved frames in the texture.
To avoid unnecessay performance problems, only one Analyze Audio node should be used per sound source.
Audio Configuration
To listen to a Ventuz Audio device you have to configure them in the Ventuz Audio Video Configuration. In the Cross Point section you can add and remove virtual audio cables. I.e. you can add a cable Ventuz A --> Ventuz A to listen to the first stereo pair of the Ventuz Audio device.
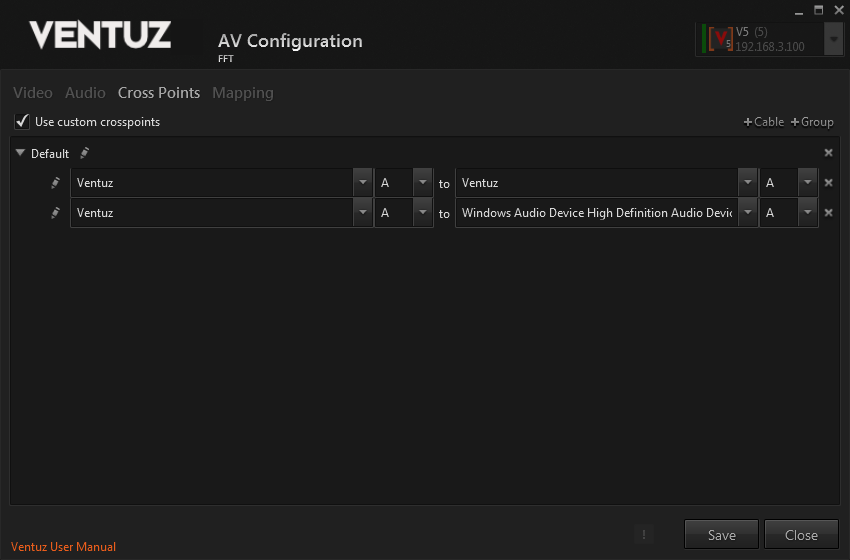
The first Cable is necessary to make the Analyze Audio node listen to audio and sound played by Ventuz. The second Cable is only necessary if the audio should be forwarded to an audio hardware in the Ventuz machine.