Substance Material
Table of Contents
 | Substance Material | Loads Substance Designer Materials in .sbsar format. |
General
WARNING: Due to the fact that the Substance Engine utilizes the same GPU as Ventuz it is impossible for us to guarantee a stall-free Ventuz rendering during Substance texture generation in the background! It is neither advised to change the input properties for a substance during runtime, the whole texture-set will be newly generated. Therefore Ventuz may STALL!
Please keep this is mind if you need to load and validate scenes in the background or if you are working in a Multi-Pipe configuration with the Director!
The Substance Material node can load so called Substances as a *.sbsar file which are created with the Substance Designer from Allegorithmic. The Substances have exposed properties which are accessible in Ventuz. With these exposed parameters you can change the appearance of the generated Texture(s) to give them a different look and feel. The accessible input parameters change for each individual Substance and the same goes for the Texture Outputs. Ventuz and the Substance Engine will automatically map and bind the generated Texture inside of the Material Node so that the Substance Material node can be used right away. The rest of the properties and handling of the node is similar to the Material node, like the Texture Stages.
Properties
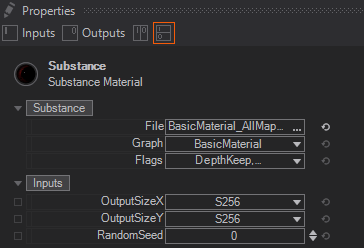
The common input properties for the Substance Material node are the File to load a so called substance (as a *.sbsar format), Graph to select a specific part/graph, if there are more than one provided by the substance, and Flags which let you select Bit Depth and Gamma value. Ventuz will already compact all grayscale textures into one single output texture as long as their semantics do match. If a loaded Substance consists of several grayscale textures like an AO and Roughness, these textures will be combined into a single texture and use the R component for the AO and the G component for Roughness to save texture stages and outputs.
Bit Depth can be set for all output textures and you can set it either to 8Bit, 16Bit or Preserve which is the default predefined setting from within the Substance. Changing the Bit Depth will affect ALL Output Textures that allow the changes and are not already predefined from within the Substance Designer/sbsar. Gamma can be set to sRGB or Linear. Changing the Gamma will affect only the textures which semantics are set to sRGB or a different Gamma value from within the Substance Designer and the ones that allow the changing of the Gamma. For example, if you force the gamma to sRGB, the NormalMap will still have its preset or own Gamma.
The Inputs Properties itself depend on the loaded Substance. They will vary and are exposed from within the Substance Designer.
It is very common to have at least the OutputSizeX/Y and RandomSeed Properties. You can change the total resolution of the whole substance textures generated and change the global random seed of the substance.
The Output Properties also vary depending on the loaded Substance. Usally you will find textures here which are already bound to the Material Stages - Texture Properties. In most cases the Outputs Texture Properties will give you a hint where to connect the texture to by reading a naming like BaseColor, NormalMap, Roughness and so on.
Per default the "Height" or "Displacement" material stage is deactivated and needs to be manually activated. This is because you would need to have a tesselated geometry to have it work properly
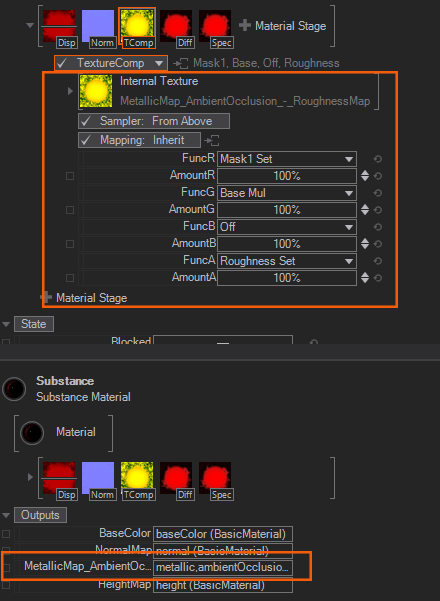
Resulting Substance Material Node
Below you can see a Substance loaded into a Substance Material Node. The substance has been loaded and the exposed property values from the Substance Designer are accessible. Also the resulting output textures have been already bound to the respective Texture Stages and the Displace Stage is disabled.
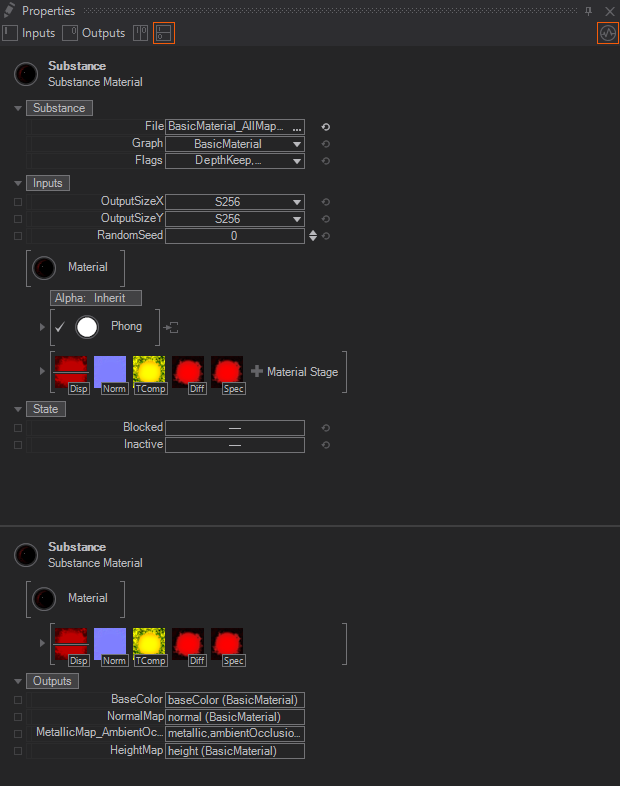
As soon as Ventuz did load a Substance and the Substance Engine has generated all the textures, the textures will be compacted. In the following example the Metallic-, Roughness- and AmbientOcclusionMap are "compacted" into one internal single Texture Stage since these textures contain greyscale informations anyway. You still have access to all single textures by using each single R,G,B or A channel.