How To Use a Cluster with Mixed Frame Rates
Table of Contents
Under certain circumstances, machines in a Ventuz Cluster setup need to run with different frame rates. Or, looking at it the other way round, sometimes machines that run on different frame rates need to join a Ventuz Cluster to take advantage of its functionality.
This page describes why this is necessary and how to configure it.
Running machines with mixed frame rates in a cluster only works in DirectX Output Mode, including implemented Headmounted Displays.
Cluster-Communication
To make Ventuz render machines act like a Cluster, different data and information is shared between them like the Cluster Clock, the Input Subsystem or some cluster sensitive nodes.
The most important one is the Cluster Clock as it creates a common time base which is needed for rendering synchronization, but also other cluster communication relies on this time base.
What is special about Mixed Frame Rates?
As stated on this page: Cluster Clock - the timing master distributes the clock across the cluster and each machine uses its global fps setting to determine the current time. So if two machines run on different fps settings, the calculated time that drives animations, movers, determines when cluster data should be executed, is different. The results are discontinuous animations, animations that appear in different speeds, touch or other data that seems to be applied with a wrong timing etc...
The solution is to bring the cluster clock to the same logical value by using the Mixed Frame Rate multiplier.
Frame Rate Multiplier
To make a cluster with mixed frame rates work correctly, the cluster clock has to be matched. More specific, it has to be set to the least common multiple. The global FPS setting is used to calculate the local timing from the cluster clock, so the FPS setting has to match the graphic cards' refresh rate. Then the frame rate multiplier is used to bring it to the least common multiple of the machines.
The frame rate multiplier increases the steps of the cluster clock to a level that the machines have in common, so each machine can use the multiplier and the machines fps setting to calculate its correct local time base.
The frame rate multiplier is set in the output stream options.
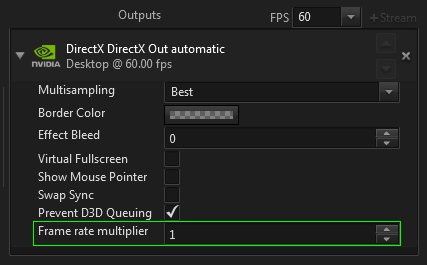
Example: A cluster of two machines should be used. Machine one uses a VR headset that runs on 90Hz, as output. Machine two drives a display that can not run on 90Hz, but has to run on 60 Hz. The least common multiple of 90 and 60 is 180. So machine one has to be set to 2 x 90 Hz, Machine two has to be set to 3 x 60 Hz.
Increasing the cluster clock steps with the multiplier not only changes the value of the clock. It actually increases the internal validation steps in the render engine for it to be able to apply the correct timing. The rendering, of course, stays at the machines refresh rate, so in the above example, machine one renders 90 frames per second and machine two renders 60 frames per second.
Timing Master and Interaction Master
When input devices are involved, it is essential that the Interaction Master is also set to be the timing master. In general, it is not crucial whether the machine with the lowest or highest frame rate is the clusters' timing master.
Performance Statistics
When a frame rate multiplier larger than 1 is used, it is displayed in the performance statistics next to the framerate.

Example
An example for a setup that involves machines running at different frame rates but still a Cluster is needed was already introduced above. The HTC Vive and its controllers are used to create a VR Experience. A second machine runs a display wall so an audience can watch the happenings from a third person perspective. As the user interacts with the Ventuz scene using the Vive controllers, the touch information has to be passed to the machine that runs the display wall. The HTC Vive runs on 90Hz. Unless the involved display wall is capable of running on 90Hz, this results in a mixed frame rate setup. For this example, the display wall runs on 60Hz.
The FPS setting for each machine is set to the refresh rate of the output device. So for machine one, it is set to 90 fps, for machine two it is set to 60. The least common multiple of 60 and 90 is 180. So the multiplier on machine one is set to 2 (2x90fps), the other one to 3 (3x60fps).
When the user triggers touches in the scene, this information should be passed to the other machine via the Input Subsystem. So the machine that is connected to the HTC Vive is configured to be the Interaction Master.
As described in the section above, it is essential for the Interaction Master to be the Clusters' Timing Master. So this machines MachineID has to be configured to be the lowest in the Cluster - typically 1.
Tweak: The HTC Vive actually does not run on 90Hz, but around 89.5Hz. To assure stable synchronization, it is helpful to override the EDID with 90 Hz.