Property Editor
Table of Contents
The Property Editor is probably the place a user spends most of his time. As soon as an operator cues a template, Director creates a template instance of that template. Think of the template as a blueprint and the instance as version of that blueprint where all the values have been filled out. If an operator cues the same template multiple times but with different values, each cueing creates an instance and the original template as defined in the Ventuz scene is never changed.
The Property Editor changes its appearance to match data values of the cued template instance. The following image shows the Property Editor in three different states. In the left version, no template is cued and therefore the Property Editor is empty. Once a template is cued, a header and footer become visible as well as the data fields for the template.
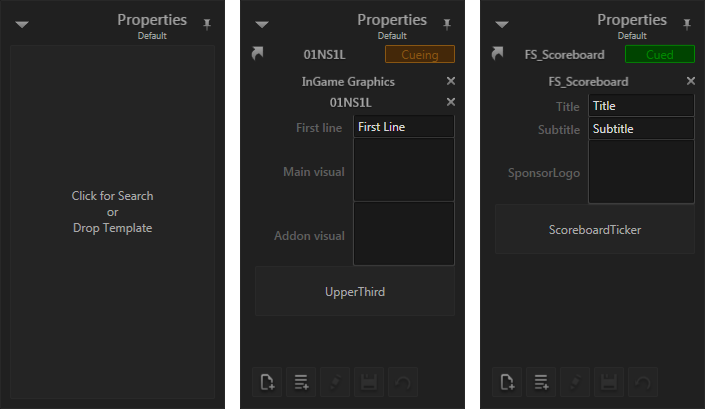
Header
The header contains status information about the current template instance:
- The Symbol in the top-left corner represents the type of data. This will later be explained in the chapter on Content References.
- The text in the center represents the instance's name.
- The box in the top right corner shows the current state, cueing (i.e. loading) in the center version and cued (i.e. ready to go) in the left.
Content
The actual content of a template instance uses most of the space in the Property Editor. Which controls will be shown depends on the data fields the designer of the template has exposed to the end-user. A string will result in a text box, a numeric value in a numeric up down control or a slider, an image in a placeholder box and so on. The Property Editor dynamically generates a user interface that looks as if the designer of the template would have programmed it specifically for that template.
Templates & Sub-Templates
Let's take a closer look at the content of the template instance shown in the middle of the screenshot above:
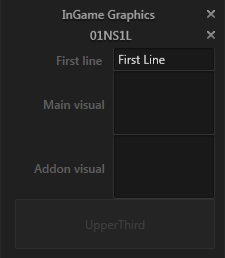
The label "InGame Graphics" as well as "01NS1L" represent templates. Ventuz Director uses a highly flexible system of templates and sub-templates. Templates can have slots for optional additions that can be added and removed from it's parent template. For example: imagine a scoreboard that has an optional sponsor area that moves out of the scoreboard and sticks to its side. The scoreboard would be one template and the sponsor area a sub-template for that template. It is up to the operator to extend the original template with the sub-template or not!
Such an extension slot is represented by a light gray box. In the example, the box at the bottom of the content visualizes that a sub-template of the type "UpperThird" can be inserted here. This can be done by clicking on the box and a selection of fitting templates will be presented. The inverse operation is also simple: To remove a sub-template, click on the cross to the right of the template name. In the example, both the "InGame Graphics" and "01NS1L" template can be removed.
Assets
As stated before, Assets are represented by placeholder boxes. In the example above, both "Main visual" and "Addon visual" can each hold an image. Either drag and drop an image from the Visual Browser or click on the empty box to again open a selection of fitting images.
Modifications
If any data fields are changed, a red bar will appear to the left of the respective field. That visualizes the value that is different from the original. Those changes can be saved or reverted using the respective buttons in the footer.
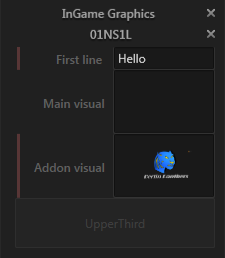
Events
Inside the Property Editor, triggerable events on a template are represented as buttons. While something is cued, that event will only be performed on the cued data and therefore is not visible on screen! To trigger an event on-air, switch to the On-Air Editing Mode.
Footer
The footer can hold certain sets of buttons. The appearance can be configured in the window settings.
- The show control for this specific channel.

- Controls for Storing and Re-using Content, all of which will be discussed in later chapters.
 From left to right:
From left to right:
Window Settings
The window settings holds options to customize the footer of the property editor window and enable channel specific options. They are located in the top right corner of the window.
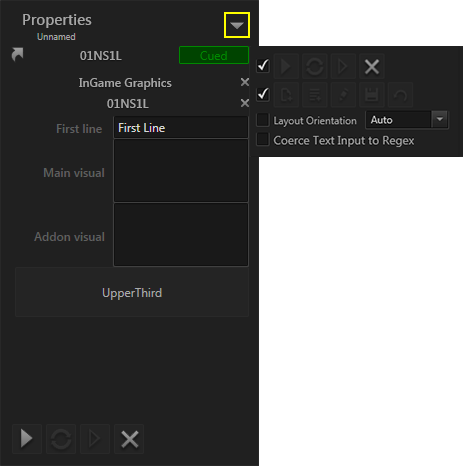
- Layout Orientation: Can be set to Auto, Horizontal or Vertical. In Auto mode the layouting changes from vertical to horizontal based on the aspect of the window. Horizontal and Vertical always layouts the properties in the set direction.
- Coerce text Input to RegEx: The property editor validates Regular Expressions set on a data item. When Coerce is set to false and the expression does not match, it will be indicated to the operator by a red frame. If Coerce is true, data that does not match can not be entered to the text field at all. One exception to that is: If the regular expression just restricts the amount of characters in a string, a string that is pasted to the text field is truncated to the maximum allowed characters.
Any parts of the Property Editor that have not been mentioned in this chapter are not relevant for the basic workflow of cueing/taking a template and will be explained later in the chapter on Content References.