Table of Contents
Hatch
 | Hatch | Creates non-realistic rendering. 3D Elements look like they are sketched or hatched. |
The Hatch Node is used to create a non-realistic shading on the 3D Elements it is applied to. The actual shading is done by a Material Node using a Hatch Shading Material Stage. The Hatch Node is only needed when you want to use a custom texture for the hatch shading.
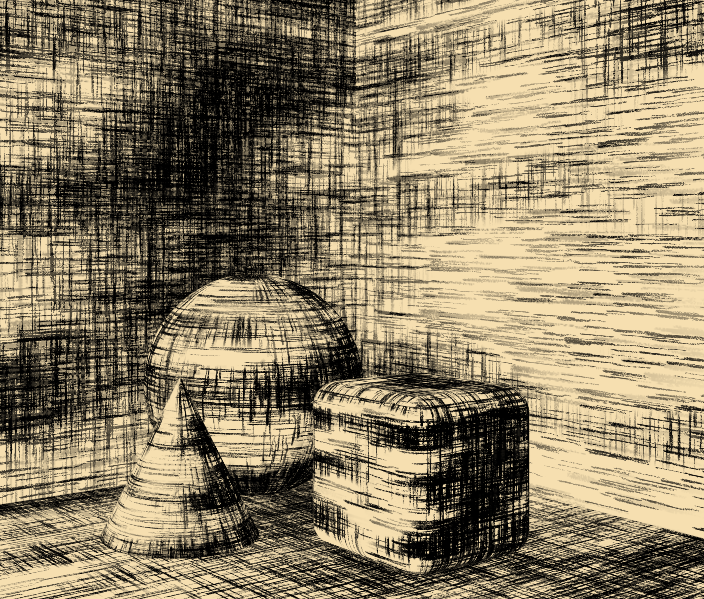
Hatch Shader Material Stage
To create a hatch effect you need a Hatch Shading Material Stage on a Material. There you can adjust some options of the shading.
The Hatch Shader basically multiplies the current color of the Material with the PaperColor. The darker a Material gets due to the lighting, the more InkColor from Hatches will be applied. Hatches are samples of the defined Hatch Texture.
Preset offers you four default Hatch Textures to use: cross, lines, curves and letters. If you choose any of these you do not need a Hatch Node. When set to Hatch Texture it uses the Texture created by the nearest parent Hatch Node. If there is none, the Hatch Shading Material Stage does not affect the shading.
Mapping defines how to apply the textures onto the objects. You can use one of the two UV Sets of the geometry or a Triplanar Mapping, based on the Object, World or Camera Coordinate System. Scaling changes the size of the applied hatches.
MipMapBias changes the starting MipMap of the Hatch Texture. The higher the MipMap, the rougher the applied Texture. The Hatch will be applied in several steps, each time getting a little rougher, starting with the least rough one in the first step.
Invert creates an inverted effect of the Hatch Shader. It does not multiply with the PaperColor and add hatches of the InkColor wherever there are dark spots, but instead it multiplies with the InkColor and adds hatches of the PaperColor wherever there are bright spots.
Specular defines whether or not to take the specularity of the Material into account.
Hatch Node
If you have defined to use a HatchTexture in the Preset property of the Hatch Shader Material Stage of the Material Node you need to place the Hatch Node in front to provide it with a custom Hatch Texture. It has options to change the behavior of the Hatch provider.

StrokeImage defines the File Path to the Hatch Texture. With Strokes you can define how many Strokes are stored in the image. You can use up to 16 different Strokes. If BlackOnWhiteInput is set to true the Hatch Shader will interpret Black Color in the Texture as Strokes - this is useful for the InkColor.
Steps will define how many steps the Shader should go through with this texture - each step will create less and less rough strokes. With the TextureSize property you can adjust the size of the Texture in the GPU Memory. Mipmaps defines how many mipmaps to generate for each hatch.
The properties in the Pattern Category change the behavior of the hatches themselves. RandomSeed defines the seed for the randomization process in the Shader. When set to something else than 0 it will look the same on every load when all other properties are the same. When set to 0 it will look differently each time the scene is loaded.
WidthAverage and HeightAverage define the average height and width respectively while WidthRandom and HeightRandom define the maximum variance.
FlipPattern defines when to use horizontal and vertical strokes depending on the step the shader is currently calculating.
Hatch Texture
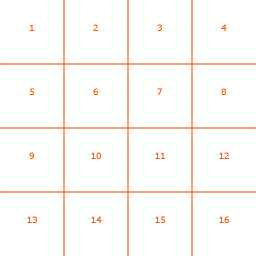
To create a Hatch Texture, you need to have a squared texture that has strokes on a 4x4 pattern on it. If you do not want to use all 16 strokes you still need to align the used ones in the 4x4 pattern. By changing the Strokes property of the Hatch Node you can avoid empty parts of the texture. The following image illustrates in which order you should add the strokes.