Scene Statistics
The Scene Statistics dialogue provides information about the nodes and their occurrence that have been used in the scene. It shows which scene components and resources use how much memory space. Additionally all assets that are used in the open Ventuz scenes are listed.
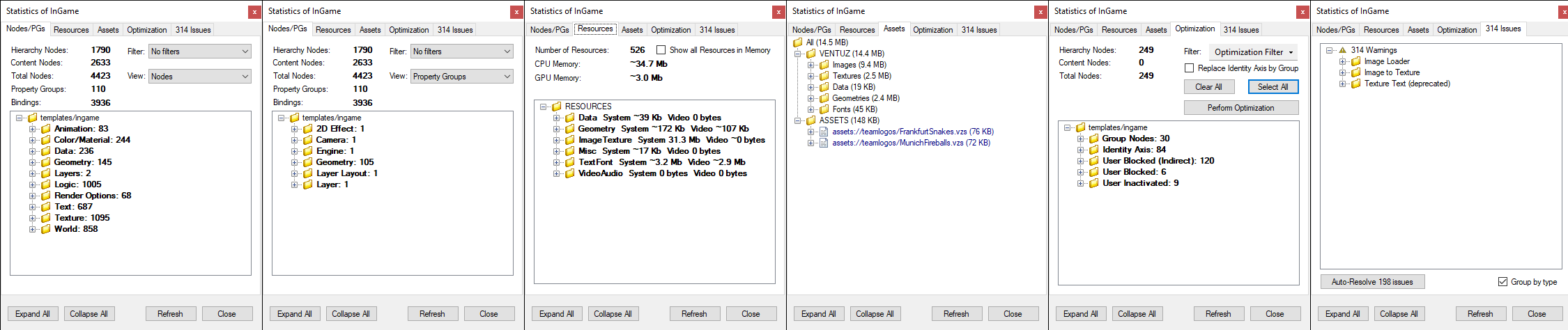
The Statistics dialogue is separated into five parts.
Except in the Resources tab double-cliking on an entry in the tree will navigate you to the according node in the scene.
Nodes/PGs
The Nodes/PGs tab gives an overview of the nodes and property groups used in the currently open scene.
Below the summery all used nodes are listed according to their Toolbox category. The number behind the category folder is the total number of nodes from this category in the scene. If one expands the folder, all used node types and their occurrence are listed. It is possible to double-click on an entry and the Hierarchy and Content Editors will navigate to the according node in the scene tree.
The View can be switched to see not only the Nodes but the used Property Groups.
Additional filters can be applied to list e.g. deprecated nodes, see the following list for more.
| Filter | Function |
| No Filters | All Nodes of the active scene |
| Hierarchy Only | Only Hierarchy Nodes |
| Content Only | Only Content Nodes |
| Full ScenePort Hierarchy | All Nodes from the active and all nested Scenes |
| Deprecated only | Only Nodes of previous Ventuz versions that are no longer available |
| Live-Linked only | Only Nodes with an active Live-Link |
Resources
The Resources tab shows the memory usage of all scene resources. If the Show all Resources in Memory option is enabled, all resources of all loaded scenes will be listed; otherwise only those of the active scene. The resources are assigned to different categories/folders:
- The TextFont category contains all resources which are somehow related to text rendering like texture and mesh fonts, font files, the texts itself, etc.
- Data contains all resources created by Xml, Excel and Text files but also the Shader related data.
- Geometry lists all resources built by the Geometry primitives and the Mesh Loader node.
- ImageTexture lists all resources that are related to images and textures. These are resources built by all the image and texture loader/creator/manipulator.
- VideoAudio lists all resources that are needed for video/movie and audio playback.
The memory usage of the resources is separated into the System and Video memory pools. System represents the normal CPU memory and Video the memory on graphics cards.
Assets
The Assets tab lists all assets that are currently loaded into memory. Every asset entry lists all those nodes which reference this asset. The assets are sorted according to their data pools in the Project folder. Here it is possible to replace certain assets for the whole scene or single nodes or to perform an automatic search and replacement for missing assets. Just press the on a tree node to get a context menu with the possible options.
Optimization
In the Optimization tab it is possible to detect and remove unnecessary nodes. Optimizing a scene can improve its performance and reduces size. It makes sense to check the scene for unnecessary nodes especially if one works with lot of copies of the same (Hierarchy) Container.
The Optimization process is destructive and cannot be undone! The only possibility to go back to pre-optimized state is by saving the scene before!
Following optimization filters are available:
Alpha is Zero
Show Alpha, Solid Color or Material nodes in general with AlphaVaue = 0% and Block on full transparency enabled (both properties must not be bound to other nodes, SceneData or exposed to Scene level). Such nodes block the node hierarchy below and it is not rendered anymore thus it is unnecessary.
Alpha is Full
Show Alpha nodes that have an unbound AlphaValue set to 100% and an unbound Blocked property. Such nodes do not affect the rendering and can be removed.
Identity Axes
Unbound Axis nodes which have all properties set to default are so called identity axes and do not affect rendering if they do not directly lie beneath an Arrange node. It is save to remove them or, if you need them as structural element, to replace them by Group nodes (check the Replace Identity Axis by Group option).
Invisible Subtrees
With this filter it is possible to detect hierarchy trees that do not end with a rendering node (a node that has effect on the visual output like Text or Set 3D Mask). Such subtrees can be removed. Note that some hierarchy nodes do not affect the rendering directly like Material or Geometry but affect it indirectly in a different part of the scene tree. Two examples are the Volume and the Mirror node. Tree branches ending with these nodes are not detected as invisible. Subtrees that provide values to other parts of the scene are neither classified as invisible.
User Blocked
Hierarchy nodes with an unbound Blocked property set to true do not have effect on rendering and also block their child nodes. The affected nodes are grouped in two categories: User Blocked and User Blocked (Indirect).
Such subtrees can be usually removed but there are some exceptions:
- Blocked Hierarchy Container with content are not taken into account as they may contain Content nodes with necessary logic (such nodes are not deactivated if their parent Hierarchy Container is blocked).
- If nodes within such a blocked subtree provide values to other parts of the scene, the blocked subtree down to such a provider node is not taken into account.
- Indirectly blocked Hierarchy Container with content are not taken into account.
User Inactivated
Inactive nodes that neither have the Inactive nor the Blocked property bound can be removed as they do not affect the rendering.
Content Node Islands
This filter shows Content nodes which do not have any binding to the Hierarchy tree, Scene Data, Template Data or "sender" nodes like OSC Out, Sound, Script, etc. Values generated by these nodes are not consumed and the nodes are redundant.
Binding Sink Content Nodes
This category of nodes is similar to the "content islands" except that they have a binding from the Hierarchy tree that provides them with values.
Group Nodes
Group nodes only have an organizing function in the Hierarchy Editor if their properties are not bound. They can be safely removed.
Suboptimal Spreader
The Spread node internally multiplies the attached node tree by the number specified by Max. The property Count defines how many of these copies are displayed. If Count is not bound and lower than Max it makes sense to reduce Max to the value of Count to improve performance and memory usage.
Empty Text Provider
Empty Text Layout and Text Effect nodes that do not have the Text respectively TextSource property bound can be removed. This is especially helpull as text resources can get pretty huge and loading a font that is not used at all does not make sense.
Empty File Loader
File or Asset loader nodes like Text, Texture Loader or Sound that have an empty File property that is not bound can be removed as they do not load and provide any resources for further processing.
Analyze Sealed Containers
With this filter enabled sealed Container are evaluated but the found issues will NOT be optimized!
It is additionally possible to convert unbound Identity Axes to Group nodes by checking the Replace Identity Axis by Group option and selection the Identity Axis filter. This can be quite helpful as Ventuz operator tend to use Axes as an element in the hierarchy tree just to improve the structure. But an Axis is pretty expensive compared to a Group node.
When clicking the Perform Optimization you will be asked to save a backup of your scene. After this the unnecessary nodes will be removed.
Note that an optimization step can produce a scene which shows further optimizations opportunities. E.g. removing a blocked subtree can generate an invisible subtree. With such an iterative optimization process it is more comprehensible why certain scene elements have been removed.
Issues
The Issues tab lists all nodes that are causing issues. Scenes from older Ventuz versions can contain nodes that do either not work at all any more, cause errors in the rendering or only function in a limited fashion.
- Fatal: Nodes in this section do not work anymore and must be replaced.
- Error: Nodes in this section are not compatible with new features or technologies and should be replaced. Note that the Nodes still work in general and will not cause errors in Legacy Mode.
- Warning: Nodes in this section do work, but do not take advantage of the latest technologies. While they will not break other features or cause side effects, they should be replaced to unleash the full potential of the new version.
Hovering over the Nodes in the Issues tab shows a tooltip with a hint on how to node could be replaced.
You can also use the Auto-Resolve issues, which will try to solve issues automatically, for example exchanging deprecated nodes with new ones.
If the scene tree is modified by adding or deleting any nodes, press the Refresh button to update the statistics.