Z-Testing
 | Z-Testing | This node modifies the depth information that is written by geometries into the depth buffer (Z-Buffer). |
The Z-Testing Node is an Alias of the Material Node. It changes one of the tests that is performed to decide whether a fragment of an object is rendered or not. The Material Node has other options that are documented on the respective pages (see table below for more information).
General
The Material Node controls the appearance of the surface of each rendered Object placed as a child in the Hierarchy. It consists of several options that can be added to its list of properties to overwrite the according options. The options are available under Material Node's Tabs that are represented by the button bar on top of the Material Definition in the Property Editor.
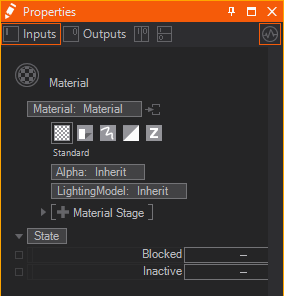
Generally these tabs exist:
| Standard | affects the overall transparency | |
|---|---|---|---|
changes how light affects the color of a surface | |||
adds textures and material stages that change the shading | |||
| Shadow Options | changes the shadow related behavior | |
| Drawing Style | applies a draw mode for geometries (lines, solid, sprites etc.) | |
| Blending | changes the write mode to specified color channels | |
adjusts the blending of geometries onto the background | |||
| Testing | applies a custom test against the object's alpha | |
defines a custom occlusion test for the geometry |
To show the options of a tab simply click on the according button. You can insert options by clicking on the Property Group's entry and choosing the wanted options from the dropdown.
All options that you do not adjust in a Material node are inherited by the Default Material or the Material node in front.
Icon and Decoration
In general the Icon rendering can be changed by switching between Sphere, Quad and Torus at the bottom of the Properties Editor or via .
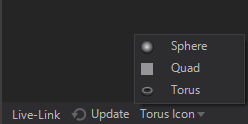
Based on the Property Groups that are used inside a Material Node the Icon may change.
| Rendered Preview | if only Property Group's in the Standard or Shadow Options tab are used. |
|---|---|---|
| Rendered Preview with light blue decoration | if Property Group's in the Standard or Shadow Options tab are used together with any other Option like a certain Draw Mode or a certain Blending |
| Dedicated Option Icon | every Material Option has it's own dedicated Icon, that is shown whenever no other Property Group in any other tab is used. |
Extraction
Material Definition
A Material node is a Hierarchy Node by nature. But it can serve as a Material Provider as well. This is useful whenever you want to use the same material in different locations of your hierarchy or once you have Hierarchy Nodes that need more materials than one applied to it (e.g. the Particle System Node). The below image shows both a Material Node and an extracted Material Node Provider together with a receiving Material Node.
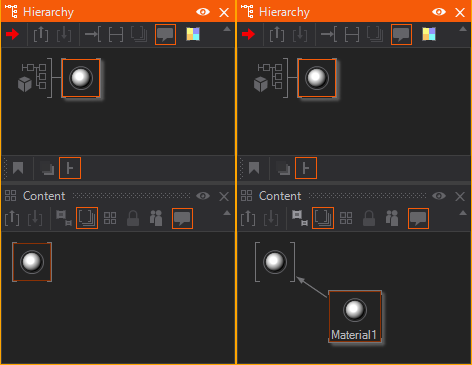
You can either place the Material node in the Content Editor to create an unbound Material Provider node. Or you can use the extract button  on any node that hosts a Material Definition to extract it to a provider that can be re-used on other nodes.
on any node that hosts a Material Definition to extract it to a provider that can be re-used on other nodes.
Material Options
Since a Material consists of several options sometimes you want to extract some of them to a seperate Hierarchy Node. This way you can apply single Material Options to other parts of the Hierarchy Tree when already added to the Material. Just use the extract buttons  next to the Material Options.
next to the Material Options.
The Z-Buffer (also called Depth Buffer) is used to determine object occlusion during Rasterization. During rendering of a triangle, the Z-value of a given pixel is compared to the value stored in the Z-Buffer. Based on the Z-testing function, the triangle either is allowed to overdraw the pixel or not.
The default behavior is to accept pixels that have a Z-value that is smaller or the same as the value in the Z-Buffer, making objects closer to the camera occlude objects which are farther away. While it may seem weird at first to ever use something that is different from the default (and in the majority of cases this is the best option), using different comparison functions can be used to create interesting rendering effects or prevent rendering artifacts from happening.
Z-Testing Options
The Z-Testing Node can influence the above decision in multiple ways. You can either use a simple set of options or an advanced one.
Simple
The Test property can be deactivated to do no Z-testing at all for all children nodes. The Write property can be deactivated to just perform the Z-test but not update the values in the Z-buffer once a pixel is rendered.
In certain situations like rendering a wireframe overlay over a solid object, visual artifacts due to Z-fighting problems can be avoided by adding a small offset to the Z value calculated for a pixel. This offset is only used for the Z-testing comparison. If the pixel is drawn and updates the Z-Buffer, the original Z-value will be used. This offset is specified by a fixed offset called Bias.
Advanced
The Advanced Z-Testing options can change the test function itself to one of the following settings:
- Inherit: The comparison function is inherited from a parent Z-testing node or the default (Less Equal) if non exists.
- Always: A pixel is always drawn, no comparison to the value in the Z-Buffer is performed.
- GreaterEqual: A pixel is drawn if its depth value is greater than or equal to the corresponding value stored in the Z-Buffer.
- NotEqual: A pixel is drawn if its depth value is not the same as the corresponding value stored in the Z-Buffer.
- Greater: A pixel is drawn if its depth value is greater (not equal) than the corresponding value stored in the Z-Buffer.
- LessEqual: A pixel is drawn if its depth value is less than or equal to the corresponding value stored in the Z-Buffer.
- Equal: A pixel is drawn if its depth value is exactly equal to the corresponding value stored in the Z-Buffer.
- Less: A pixel is drawn if its depth value is less than the corresponding value stored in the Z-Buffer.
- Never: A pixel is never drawn.
Slope can be used similar to Bias. It is multiplied with the maximum depth value of the triangle being rendered. It can be used to adapt the offset with the distance from the camera, countering Z-Buffer resolution issues.
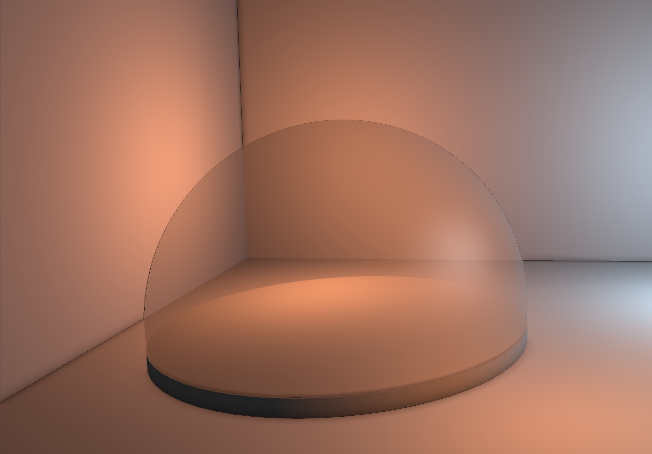
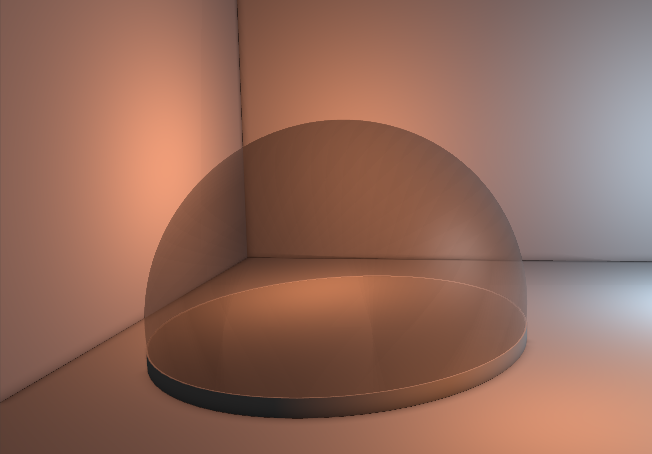
Write Normals can be turned off to prevent normals from being written. This normally is turned off only if the Write property is set to off as well. Normals are used e.g. by the Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion (SSAO) effect on 3D Layers. The SSAO would not be rendered for areas behind transparent objects, because only the depth and normals of the transparent object's surface is known. By turning off writing both Depth and Normals the SSAO is now calculated for objects behind (but not for the transparent object in the front).
| Z-Write | YES | NO | NO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal-Write | YES | YES | NO |
 |  | 
|




